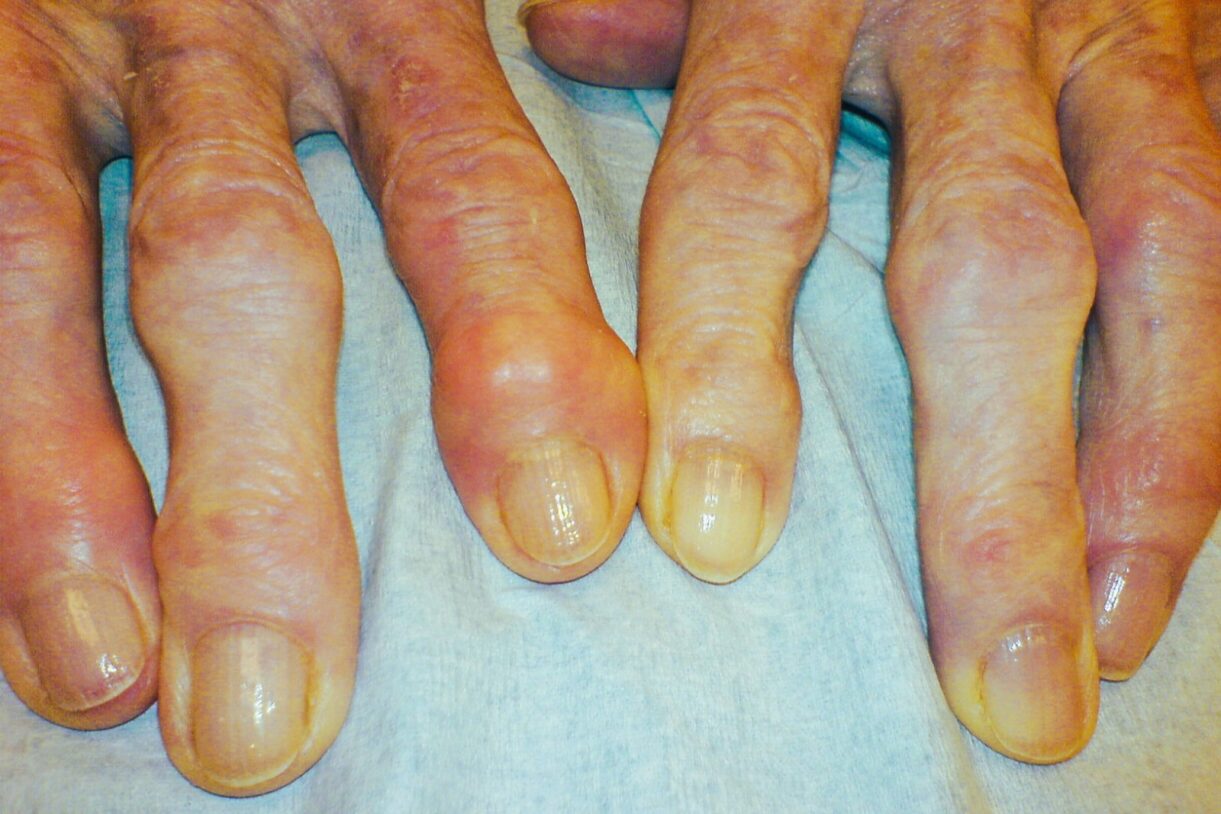
Arthritis supplement’s glaucoma effects
US researchers have discovered that some over-the-counter glucosamine supplementations are associated with increased intraocular pressure (IOP) and could contribute to the pathogenesis of glaucoma.
The research team, led by Drs Steven Lehrer from the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and Peter Rheinstein from Severn Health Solutions in Maryland, used online databases to evaluate the relationship between glucosamine, IOP and glaucoma. In UK Biobank subjects, glucosamine use was associated with increased corneal compensated IOP, which was also true in subjects without glaucoma. However, no significant association between glucosamine and IOP was detected in subjects who had a glaucoma diagnosis. In the US database MedWatch, however, glaucoma was reported by 0.21% of subjects taking glucosamine, said researchers. Meanwhile, data from Finland’s FinnGen database revealed a significantly increased risk for developing primary open-angle glaucoma (hazard ratio: 2.35) as well as glaucoma (hazard ratio: 1.95).
Although glucosamine supplementation is frequently recommended to treat osteoarthritis symptoms, its effectiveness is questionable, said the research team, concluding that it would be prudent for eyecare professionals to discover if their patients had any history of glucosamine use and advise them accordingly.